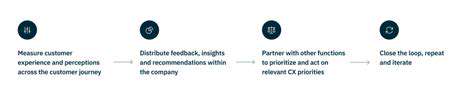
Data Migration Planning: Laying the Foundation
A robust data migration strategy is crucial for ensuring a smooth transition. This involves meticulous planning, encompassing detailed assessments of the source and target systems. Careful consideration must be given to data volume, structure, and quality to anticipate potential challenges. Understanding the specific requirements of the target environment is paramount to a successful migration.
Thorough documentation is essential for tracking progress and troubleshooting potential issues. Clear communication channels between stakeholders and teams involved in the migration process are vital for maintaining alignment and preventing misunderstandings. This phase also involves the development of a detailed timeline, outlining key milestones, deadlines, and resource allocation.
Data Validation and Transformation
Validating the integrity of the data during the migration process is essential. This involves comparing the source data with the target system specifications to identify discrepancies and ensure accuracy. This crucial step allows for the early detection and resolution of data quality issues. Processes for data cleansing and transformation need to be well-defined to ensure consistency and adherence to data standards.
Data Migration Tools and Technologies
Selecting the right tools and technologies is critical for a successful data migration. Evaluation of various options based on factors like scalability, performance, security, and cost considerations is essential. Choosing the right tools can significantly impact the efficiency and success of the migration process. Different tools cater to specific migration needs, and the right selection can streamline the entire process.
Data migration tools should be chosen based on the complexity of the migration and the specific requirements of the data being transferred. Some tools offer ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) functionalities, enabling the automated transformation of data from the source to the target environment.
Data Security and Compliance
Data security and compliance are paramount throughout the migration process. Protecting sensitive data during the transfer is critical. Implementing encryption and access controls are essential to maintain the confidentiality and integrity of the data. Maintaining compliance with relevant regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA, is crucial.
Thorough security measures are necessary to mitigate potential risks. This includes access controls, encryption protocols, and regular security audits. Regular monitoring of security measures is also required to detect and respond to potential threats.
Testing and Quality Assurance
Rigorous testing is a critical component of the data migration process. Thorough testing of the migrated data is essential for ensuring accuracy and consistency. This involves validating the data against the expected specifications and identifying any discrepancies.
Testing must cover various scenarios, including data volumes, different data types, and various data formats. Comprehensive testing ensures the reliability and accuracy of the migrated data, minimizing the risk of errors and ensuring a smooth transition.
Data Migration Timeline and Budget
Developing a realistic timeline and budget is crucial for successful data migration. An estimated timeline for the entire process, including all phases, needs to be established. This timeline will help in anticipating potential delays and adjusting resources as needed.
A detailed budget that encompasses all costs associated with the migration process, including personnel, tools, and infrastructure, needs to be defined. This budget should also include contingencies for unexpected expenses that might arise during the migration process.
Post-Migration Monitoring and Maintenance
Post-migration monitoring and maintenance is critical to ensure the long-term success of the migration effort. Ongoing monitoring of the migrated data is essential for identifying and resolving any issues that may arise. This involves tracking performance metrics, identifying anomalies, and addressing any discrepancies.
Regular maintenance activities, such as performance tuning and security updates, are also necessary to maintain optimal data integrity and functionality. This ensures the smooth operation of the migrated data in the long run.
Post-Migration Evaluation and Continuous Improvement
Post-Migration Assessment: Key Considerations
A thorough post-migration evaluation is crucial for understanding the effectiveness of the migration process and identifying any potential issues that may have arisen. This assessment should not only focus on technical aspects like application performance and data integrity, but also on the impact on user experience and operational efficiency. Understanding the user experience is vital for a successful migration, as unhappy users can lead to decreased productivity and increased support tickets. A comprehensive evaluation should include metrics for performance, user feedback, and any observed changes in operational processes.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be established prior to the migration to provide a baseline for comparison after the migration. These metrics should be regularly monitored during the migration and post-migration periods to track progress and identify potential problems early. Careful consideration of the long-term impact on the business is essential for a smooth transition. This includes analyzing the return on investment (ROI) of the migration and assessing the overall efficiency gains achieved.
Addressing Challenges and Optimizing Processes
Post-migration analysis should identify any areas where the migration process fell short of expectations. This may involve bottlenecks in data transfer, unexpected performance issues with the new system, or difficulties in user adoption. Detailed documentation of these challenges is critical to prevent similar problems in future migrations.
Addressing these challenges requires a proactive and systematic approach. This can involve refining system configurations, implementing additional security measures, or optimizing operational procedures to accommodate the new system. By thoroughly understanding the challenges encountered, organizations can implement proactive solutions to ensure the long-term success of the migrated systems. This may also involve retraining users or providing additional support resources to address any user resistance to the new processes.
A thorough post-migration analysis can unveil previously unnoticed issues. These issues can include unforeseen dependencies between different applications, gaps in security protocols, and unexpected resource consumption patterns. Addressing these issues often requires a collaborative effort between IT staff and end-users.
Long-Term Sustainability and Future Planning
The post-migration evaluation should extend beyond a simple assessment of initial performance. A crucial aspect of this phase is to create a plan for ongoing maintenance and support of the migrated system. This includes identifying and addressing potential future challenges, ensuring the system is scalable for future growth, and creating a roadmap for future improvements and enhancements.
This long-term strategy is essential for ensuring that the migration effort is not just a one-time project, but a sustainable and beneficial investment for the organization. Planning for future growth and scalability is crucial to prevent the system from becoming a bottleneck as the organization expands. Implementing regular maintenance routines and establishing clear communication channels for support are also critical components of long-term sustainability.
Post-migration evaluation should incorporate a feedback loop for continuous improvement. Collecting user feedback and leveraging this feedback to refine the system and processes is essential to build a successful long-term strategy. Regular reviews and adjustments to the system are vital for optimization and to maintain a high level of user satisfaction and efficiency.