Analyzing Cost Structure and Pricing Models

Understanding Fixed Costs
Fixed costs are expenses that remain constant regardless of the volume of production or sales. These costs are essential to consider when analyzing a business's overall financial health and profitability. Understanding the level of fixed costs is crucial for setting pricing strategies and achieving profitability. Examples include rent, salaries of permanent employees, and insurance premiums. Maintaining a clear understanding of these costs helps businesses project their financial needs and make informed decisions about production levels and pricing strategies.
Analyzing fixed costs is vital for long-term financial planning. It allows businesses to anticipate consistent expenses and adjust their pricing models accordingly. Careful consideration of fixed costs in relation to variable costs and revenue projections is essential for sustainable business operations.
Identifying Variable Costs
Variable costs, in contrast to fixed costs, fluctuate in direct proportion to the production volume. These costs are directly tied to the output of goods or services. Variable costs are a key element in determining the cost per unit of production. Examples of variable costs include raw materials, direct labor, and packaging costs. Understanding the behavior of variable costs is essential for pricing decisions and production planning.
The impact of variable costs on profitability is significant. Changes in production levels directly affect variable costs, making it essential for businesses to closely monitor and manage these costs to maintain profitability.
Assessing Direct Costs
Direct costs are expenses that can be directly traced to the production of specific goods or services. Examples include the materials used in manufacturing a product or the direct labor involved in its creation. Accurately calculating direct costs is essential for determining the cost of goods sold (COGS). A clear understanding of direct costs is vital for pricing decisions and profitability analysis.
Proper allocation of direct costs is crucial for accurate cost accounting and financial reporting. This accurate assessment directly impacts the pricing strategy and the overall profitability of the business.
Examining Indirect Costs
Indirect costs, also known as overhead costs, are expenses that cannot be directly traced to a specific product or service. Examples include rent, utilities, and administrative salaries. Understanding indirect costs is crucial for a comprehensive analysis of total costs. Careful allocation of indirect costs across products is necessary for accurate pricing and cost-benefit analysis.
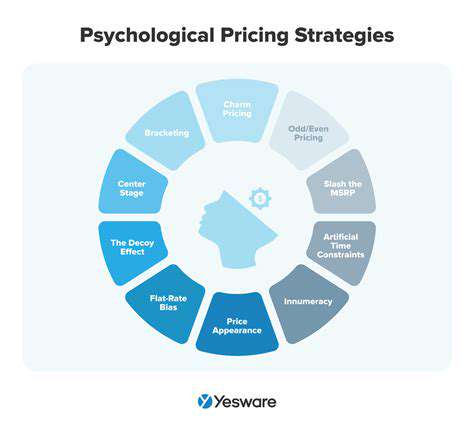
Evaluating Pricing Strategies
Pricing strategies are directly influenced by the cost structure of a business. Understanding the interplay between cost structure and pricing is essential for profitability. Different pricing strategies, such as cost-plus pricing, value-based pricing, and competitive pricing, should be evaluated in light of the identified cost structure. A thorough analysis of cost structure is essential for choosing the most effective pricing strategy.
Different pricing strategies will yield varying results, depending on the market and the specific product or service. Selecting the right strategy necessitates a deep understanding of the cost structure and the dynamics of the target market.
Analyzing Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Relationships
Cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis examines the relationship between costs, volume, and profit. It helps businesses understand how changes in sales volume affect profits, considering both fixed and variable costs. CVP analysis is a valuable tool for assessing the financial impact of various production and pricing decisions. By understanding the CVP relationship, businesses can more effectively manage their operations and improve profitability.
Using CVP analysis allows businesses to identify the break-even point, where revenue equals total costs. This critical point helps in setting pricing targets and making strategic decisions about production.