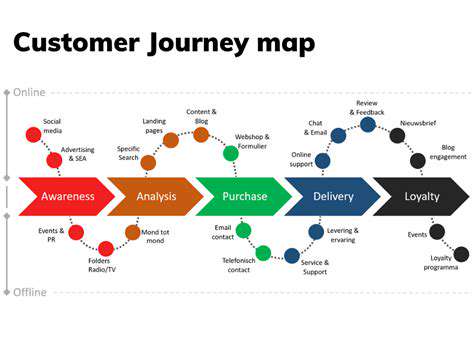
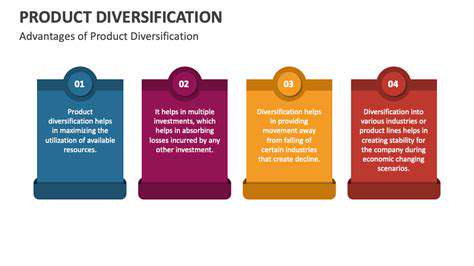
Early Days and Pioneers
The genesis of mobile payments can be traced back to the early days of smartphones, when basic mobile phone services began to evolve. Early attempts at mobile payment systems were often limited by the technology of the time, leading to slow adoption and limited functionality. These early systems often relied on SMS messaging for transactions, which was both cumbersome and prone to security vulnerabilities. Despite these limitations, these early efforts laid the groundwork for future innovations in mobile payment technology.
Early adopters and pioneers in the mobile payment space recognized the potential of this technology. They saw the opportunity for a faster, more convenient way to pay for goods and services, and they began to explore different avenues of implementation. This early experimentation, though not always successful, was critical in shaping the future direction of mobile payments. These visionary pioneers were instrumental in proving the viability of the concept, paving the way for wider adoption.
The Rise of NFC Technology
The introduction of Near Field Communication (NFC) technology marked a significant leap forward in mobile payment capabilities. NFC allows for contactless transactions, making the payment process quicker and more convenient for consumers. The ability to tap a smartphone or mobile device to a payment terminal revolutionized the way people paid for everyday goods and services.
The Growth of Mobile Wallets
The development of mobile wallets, apps that store payment information and facilitate transactions, further streamlined the mobile payment experience. These wallets provided a centralized platform for managing various payment methods, making it easier for users to pay with their smartphones. Mobile wallets also offered added security features, such as two-factor authentication, enhancing user trust and confidence in the system.
The Impact of Smartphones
The proliferation of smartphones and the increasing adoption of mobile internet access played a crucial role in the widespread adoption of mobile payments. The availability of powerful devices and reliable internet connectivity made mobile payments more accessible and practical for a wider range of users. This combination of factors created the ideal environment for mobile payment services to flourish.
Security Concerns and Solutions
As mobile payment systems became more prevalent, security concerns also emerged. Issues such as data breaches and fraudulent activities were important considerations that needed to be addressed. Security measures, such as encryption and secure payment gateways, were put in place to protect sensitive financial information and ensure the safety of transactions. Robust security protocols are crucial for maintaining user trust and ensuring the continued growth of mobile payments.
The Future of Mobile Payments
The future of mobile payments looks promising, with ongoing innovation driving the evolution of the technology. Emerging technologies, such as biometrics and AI, are being integrated into mobile payment systems, enhancing security and convenience. The integration of mobile payments with other technologies, such as smart home devices, is also likely to reshape the landscape of commerce.
Mobile Payments and Global Commerce
The adoption of mobile payments has significant implications for global commerce. As mobile payment systems become more widespread across different countries and regions, they can facilitate cross-border transactions more easily. This increased accessibility fosters economic growth and opportunities for businesses operating internationally. This globalization of mobile payment systems has the potential to create a truly global marketplace. Furthermore, this technology democratizes access to financial services for populations in regions with limited traditional banking infrastructure.
Innovative Technologies Driving Mobile Payments
Emerging Mobile Payment Technologies
The landscape of mobile payments is constantly evolving, with innovative technologies emerging at a rapid pace. One key area of development is the integration of biometrics, such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning, into payment apps. This enhances security by adding an extra layer of authentication, making transactions more secure and convenient for users. Moreover, advancements in near-field communication (NFC) technology are enabling faster and more seamless transactions, particularly for contactless payments. This reduces the need for physical cards and the associated handling risks, streamlining the payment process significantly.
Another significant advancement is the rise of mobile wallets that offer a comprehensive suite of financial services beyond basic payments. These digital platforms often include features like budgeting tools, investment options, and even peer-to-peer (P2P) money transfers. This integrated approach makes mobile wallets increasingly attractive to consumers who seek a one-stop solution for managing their finances on their smartphones. This trend is further fueled by the increasing accessibility and affordability of smartphones globally, making these services increasingly prevalent.
The Future of Mobile Payment Systems
The future of mobile payment systems is poised to be even more integrated with our everyday lives. Imagine a world where payments are seamlessly handled in the background, automatically deducting amounts from your account for recurring bills or purchases, without requiring any explicit action from the user. This level of automation relies on sophisticated machine learning algorithms that can anticipate user needs and preferences, making payments more efficient and less cumbersome. This type of intelligent automation will undoubtedly reshape the retail and service industries, making transactions even more convenient and frictionless.
Furthermore, the focus on personalized experiences is likely to continue. Mobile payment platforms will likely incorporate features that cater to individual user preferences, offering tailored payment options and incentives. This personalization will extend to security measures, adapting to individual risk profiles and dynamically adjusting security protocols. This proactive approach to security ensures a secure and personalized experience for all users, fostering trust and adoption within the mobile payment ecosystem.
The convergence of mobile payments with other technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) is also a fascinating area of potential. Imagine using AR overlays to visualize payment options within a store, or utilizing VR for secure transactions in a virtual environment. The possibilities for enhanced user experiences and novel payment scenarios are vast and exciting, promising significant changes in the way we interact with commerce.
The integration of blockchain technology could revolutionize the mobile payment ecosystem by providing enhanced transparency, security, and efficiency. The decentralized nature of blockchain could potentially reduce reliance on intermediaries, leading to lower transaction fees and faster processing times. This evolution in payment processing is critical to the continued growth and innovation in mobile payments.
Mobile payment systems will undoubtedly continue to adapt and evolve, driven by advancements in technology and consumer demand. The ongoing development of these systems will undoubtedly reshape the way we approach commerce, making it more accessible, efficient, and secure for everyone.
Addressing User Concerns and Building Trust
Understanding User Frustrations
Understanding the specific frustrations users experience with a product or service is crucial for effective problem-solving. This involves actively listening to feedback, whether through surveys, user interviews, or online reviews. Analyzing these sources can reveal recurring themes and pinpoint areas where the user experience falls short. This understanding is the cornerstone of any successful improvement strategy.
Identifying the root causes of these frustrations is often more valuable than simply acknowledging their existence. By digging deeper into the reasons behind the user's dissatisfaction, we can develop more targeted and effective solutions.
Prioritizing Concerns Based on Impact
Not all user concerns are created equal. Some issues may significantly impact the user experience, leading to lost customers or decreased engagement, while others might be relatively minor. Prioritizing concerns based on their impact on user satisfaction and business goals is essential for allocating resources effectively.
A clear understanding of the potential impact of each concern allows for a focused approach to problem resolution.
Developing Solutions that Address Root Causes
Simply addressing symptoms won't solve the underlying problems. Instead, we must delve into the root causes of user concerns to develop effective and sustainable solutions. For example, if users are frustrated with slow loading times, investigating the underlying technical issues and implementing necessary optimizations will provide a more enduring resolution than simply providing a faster loading screen.
Implementing and Testing Solutions
Once potential solutions are identified, they must be implemented carefully and rigorously tested. This process involves pilot programs, A/B testing, and feedback loops to ensure that the solutions are effective and align with user needs. Continuous monitoring is crucial to detect any unforeseen consequences.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Solutions
Effective solutions must be measured to ensure they are meeting the needs of the users. This involves establishing clear metrics, such as user satisfaction scores, conversion rates, and customer retention rates, before and after implementing the solution. Measuring the outcomes allows for a clear understanding of the impact and future refinements.
Communicating with Users Throughout the Process
Transparency and open communication with users throughout the problem-solving process are vital. Regular updates, feedback mechanisms, and acknowledging user concerns foster trust and keep users informed about progress and any potential delays. This builds positive relationships and increases user engagement.
Open communication channels are essential for gaining further insights and ensuring that the solution aligns with user expectations.
Building Trust and Maintaining a Positive Relationship
Addressing user concerns demonstrates a commitment to user satisfaction and builds trust. Actively listening to feedback and taking action on legitimate issues shows that the company values user experience, leading to stronger customer relationships and brand loyalty. This is critical for long-term success.
Ultimately, addressing user concerns and building a positive relationship is an ongoing process. Continuous monitoring, feedback collection, and iterative improvements are key to maintaining user satisfaction and fostering a strong brand reputation.