Optimizing Images and Media for Speed

Optimizing Image File Sizes
Reducing the file size of images without sacrificing quality is crucial for website performance. Larger image files take longer to load, impacting user experience and potentially leading to higher bounce rates. Employing appropriate compression techniques, such as lossy compression for images suitable for web use, can significantly reduce file sizes. Choosing the correct file format—JPEG, WebP, or PNG—is also essential. WebP, for instance, often provides better compression than JPEG while retaining quality.
Choosing the Right Image Format
Selecting the appropriate image format is vital for web optimization. JPEG is excellent for photographs, offering good compression. PNG is better for graphics and images with sharp lines or text. WebP, a newer format, generally offers superior compression and quality compared to both JPEG and PNG, making it an ideal choice for modern websites.
Understanding the nuances of each format is key to making informed decisions. Consider the specific requirements of your images and choose the format that best balances quality and file size.
Image Dimensions and Aspect Ratio
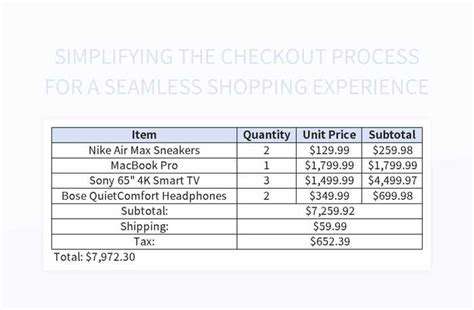
Optimizing image dimensions is paramount for website performance. Images should be sized appropriately for their intended use on the page. Using images that are too large will slow down page load times, negatively impacting user experience. Using responsive design techniques ensures images scale seamlessly across different screen sizes and devices, preventing wasted bandwidth and ensuring optimal viewing.
Image Alt Text and Descriptions
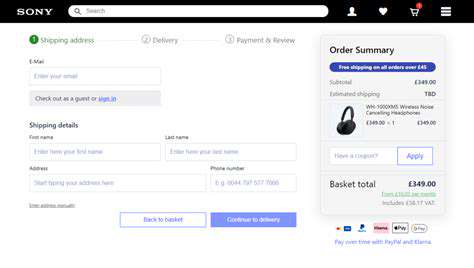
Including descriptive alt text for images is essential for accessibility and SEO. Alt text provides context for users who can't see the image, such as those using screen readers. Meaningful alt text improves the user experience and is also helpful to search engines, improving your site's visibility in search results. It's crucial to provide accurate and concise descriptions of the images, helping users understand their purpose and content.
Using Image Placeholders
Implementing image placeholders, like loading spinners or placeholder graphics, enhances user experience by giving immediate visual feedback during image loading. This prevents an empty space from appearing on the page, where the image should be, while the image downloads. Using appropriate placeholders minimizes the perceived loading time and maintains a positive user experience.
Image Delivery and Caching
Efficient image delivery and caching mechanisms significantly improve website performance. Using a content delivery network (CDN) can distribute images across multiple servers, reducing latency and ensuring fast loading times. Caching images on the server side helps reduce the load on the server and improves the response time for future requests for the same image. Implementing these strategies helps in minimizing server load and ensuring high availability of your website.
Code Optimization for Enhanced Performance

Understanding Code Complexity
Code complexity, in the context of software development, refers to the difficulty in understanding, maintaining, and modifying a piece of code. High complexity often leads to increased development time, higher error rates, and reduced code readability. Understanding the factors contributing to complexity is crucial for identifying areas for optimization.
Identifying and quantifying code complexity is essential for targeted optimization efforts. Techniques like cyclomatic complexity analysis can provide valuable insights into the potential for errors and the overall structural intricacy of the codebase. This understanding is fundamental to developing efficient and maintainable software.
Optimizing Data Structures and Algorithms
Choosing appropriate data structures and algorithms is paramount for performance. For example, using a linked list instead of an array for frequently inserting or deleting elements can significantly improve the speed of operations, particularly in specific scenarios.
Employing efficient algorithms, such as binary search over linear search, can drastically reduce the execution time of code, particularly for large datasets. This optimization is critical for applications that require quick responses and high throughput.
Leveraging Language-Specific Features
Different programming languages offer unique features that can significantly impact performance. Understanding and utilizing these features can lead to substantial optimizations.
For instance, using built-in functions for common tasks like string manipulation or numerical computations can often be more efficient than writing custom code. Mastering these language-specific tools is key for building high-performance applications.
Profiling and Benchmarking
Profiling tools provide insights into the performance characteristics of code. They identify bottlenecks and areas where code spends the most time executing, enabling targeted optimization efforts.
Benchmarking different approaches to problem-solving helps in choosing the most efficient solution. Comparing the performance of various algorithms or code segments allows developers to objectively evaluate and improve their code's execution time.
Employing Caching and Memory Management
Caching frequently accessed data in memory can drastically reduce the time required to retrieve that data, improving overall application performance. This is particularly important for applications that need to access the same data repeatedly.
Effective memory management techniques are crucial for avoiding memory leaks and ensuring that resources are used efficiently. Proper memory management prevents performance degradation and helps prevent application crashes. Understanding garbage collection mechanisms and manual memory management strategies is essential for optimization.