Measuring the Impact on Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV)

Assessing Customer Perception Shifts
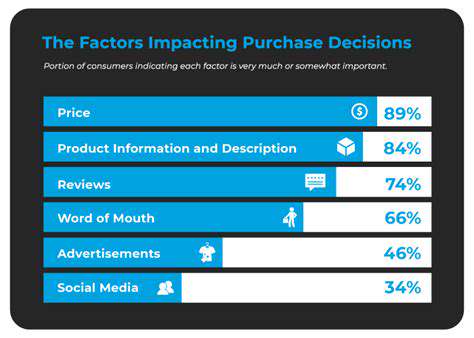
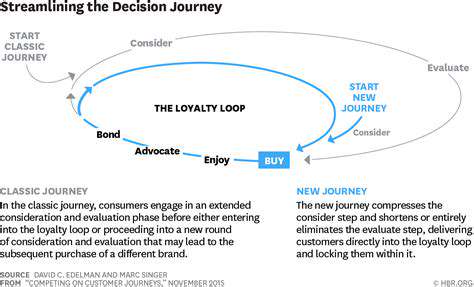
When businesses introduce changes - whether launching new products, updating services, or altering marketing approaches - understanding shifts in customer perception becomes mission-critical. Effective measurement requires multiple approaches: structured surveys, carefully moderated focus groups, and systematic analysis of feedback across all customer touchpoints. Psychological factors in decision-making often explain why customers react certain ways to changes.
Social media commentary, online review patterns, and direct customer service interactions offer particularly rich data sources. These unstructured feedback channels frequently reveal authentic customer sentiments that structured surveys might miss, providing crucial context for quantitative metrics.
Tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Several vital metrics require consistent monitoring:- Customer acquisition cost (CAC) trends- Changes in customer lifetime value- Churn rate fluctuations
Digital behavior metrics like website traffic patterns, conversion funnel performance, and engagement levels (time on site, pages per visit) complement these financial KPIs. The most insightful analysis comes from correlating behavioral data with financial outcomes to understand the full impact of changes.
Analyzing Sales Data
Sales metrics provide the most direct measurement of customer response:- Volume changes by product line- Shifts in average order value- Conversion rate movements
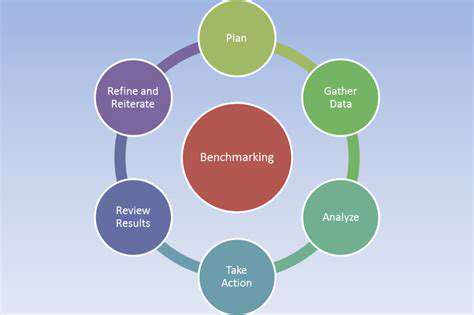
Seasonal adjustments and market trends must be accounted for when interpreting sales data to isolate the true impact of specific changes. Comparative analysis against industry benchmarks often provides valuable context.
Examining Customer Churn Rates
Churn metrics serve as a sensitive early warning system. Sudden increases in cancellation or non-renewal rates frequently indicate problems with recent changes. Cohort analysis (tracking groups of customers who joined at similar times) proves particularly valuable for understanding churn patterns.
Retention metrics should be segmented by:- Customer tenure- Product/service type- Geographic region
Evaluating Customer Satisfaction Scores
CSAT (Customer Satisfaction Score) tracking requires careful implementation:- Consistent survey timing- Representative sampling- Comparable question phrasing
CSAT trends should be viewed alongside other metrics - sometimes satisfaction scores remain stable even as purchasing behavior changes, indicating deeper issues.
Qualitative Feedback and Focus Groups
Structured qualitative research methods provide depth to quantitative findings:- Moderated focus groups with diverse participants- In-depth ethnographic interviews- Open-ended survey responses
Thematic analysis of qualitative data often reveals unexpected insights about why changes succeed or fail with different customer segments.
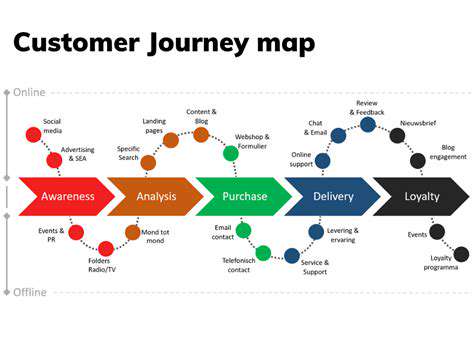
Comparing Pre- and Post-Change Data
Effective comparison requires:- Sufficient baseline data collection- Control groups where possible- Statistical significance testing
Multivariate analysis helps separate the impact of specific changes from other influencing factors in dynamic business environments.
Demonstrating Reduced Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC)

Understanding the Concept of Reduced Customer Acquisition
Strategic customer acquisition focuses on efficiency rather than reduction. The optimal approach balances acquisition spending with customer quality and lifetime value. Key considerations include:
- Channel cost-effectiveness analysis- Conversion rate optimization- Targeting precision improvements
Strategies for Implementing Reduced Customer Acquisition
Effective tactics fall into three categories:
1. Organic acquisition enhancement:- SEO optimization- Content marketing strategy- Community building
2. Paid media optimization:- Audience targeting refinement- Creative testing protocols- Bid strategy automation
3. Retention-driven acquisition:- Referral program design- Customer advocacy cultivation- Loyalty program integration
Analyzing the Impact of Reduced Customer Acquisition
Impact measurement requires tracking:
- CAC by channel over time- Marketing-qualified lead conversion rates- New customer retention patterns
Attribution modeling becomes increasingly important as acquisition channels multiply and customer journeys lengthen.
The Role of Technology in Reduced Customer Acquisition
Key technological enablers include:
- Predictive analytics for lead scoring- AI-driven bidding systems- Cross-channel attribution platforms
The most effective tech stack integrates CRM, marketing automation, and analytics into a unified customer data platform.
Customer Segmentation and Targeting
Advanced segmentation approaches:
- Behavioral clustering- Predictive lifetime value modeling- Psychographic profiling
Micro-segmentation enables hyper-personalized acquisition strategies that dramatically improve conversion efficiency.
Measuring and Optimizing for Long-Term Growth
Sustainable optimization requires:
- Continuous A/B testing protocols- Incremental impact measurement- Scenario modeling capabilities
The most successful organizations institutionalize learning from acquisition experiments, creating continuous improvement cycles.