Defining Omnichannel and Its Value Proposition

Defining Omnichannel
At its core, omnichannel represents a holistic approach to customer engagement that bridges all communication platforms. Imagine being able to start a conversation with a company via social media, continue it through email, and finalize it in a physical store—all without repeating yourself. That's the power of true omnichannel integration. Unlike traditional multichannel setups where platforms operate in silos, omnichannel weaves these touchpoints into a single, cohesive tapestry of customer interaction.
The Importance of Customer Journey Mapping
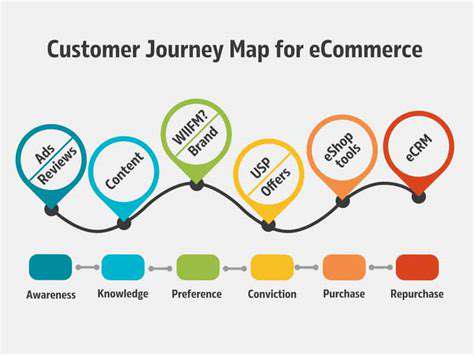
Success in omnichannel begins with walking in your customers' shoes. Detailed journey mapping reveals how prospects discover your brand, what influences their purchasing decisions, and how they engage post-sale. These insights expose friction points while highlighting opportunities to enhance interactions at every stage.
When businesses align their communications with each phase of the customer journey, they create more meaningful engagements that naturally guide customers toward conversion and loyalty.
Benefits of Omnichannel for Businesses
Adopting omnichannel strategies yields transformative advantages. Customers rewarded with frictionless experiences become brand advocates, driving organic growth through word-of-mouth referrals. This loyalty translates directly to improved customer lifetime value and reduced acquisition costs.
Operationally, consolidated systems eliminate redundant processes across departments. Teams gain efficiency by accessing unified customer data, enabling quicker response times and more informed decision-making.
Omnichannel and Personalized Experiences
The magic of omnichannel lies in its capacity for hyper-personalization. By synthesizing interaction data from all platforms, businesses develop multidimensional customer profiles. These insights power tailored recommendations that feel intuitive rather than intrusive.
When customers receive suggestions that demonstrate genuine understanding of their needs, engagement metrics soar and conversion rates climb. This level of personalization builds emotional connections that transcend transactional relationships.
Challenges in Implementing Omnichannel
Transitioning to omnichannel isn't without hurdles. Technical integration of disparate systems demands significant IT resources, while maintaining data integrity across platforms requires robust governance protocols.
Perhaps most critically, brand consistency must permeate every channel without feeling robotic. Achieving this balance necessitates comprehensive staff training to ensure all team members can deliver personalized yet on-brand experiences regardless of platform.
Measuring the ROI of Omnichannel
Validating omnichannel investments requires tracking both quantitative and qualitative metrics. Beyond traditional KPIs like conversion rates, progressive companies analyze customer effort scores and interaction patterns across channels.
The most insightful metrics often reveal how channel integration reduces customer frustration points while increasing engagement frequency. These indicators, combined with financial metrics, paint a complete picture of omnichannel effectiveness.
Measuring the Tangible Impact of Omnichannel Strategies

Quantifying the Effects
Evaluating omnichannel success begins with establishing clear benchmarks. Pre-implementation metrics serve as crucial reference points for demonstrating incremental improvements. These baselines should capture both operational metrics (like response times) and customer-centric indicators (such as satisfaction scores).
Different strategic focuses demand tailored measurement approaches. Customer experience initiatives might prioritize sentiment analysis, while operational streamlining would emphasize efficiency gains. The key lies in aligning metrics with specific business objectives.
Identifying Key Performance Indicators
Selecting the right KPIs transforms abstract concepts into actionable insights. The most effective indicators reveal not just what changed, but why those changes matter to the business. They should connect directly to strategic priorities while remaining simple enough for organization-wide understanding.
Balancing leading indicators (predictive metrics) with lagging indicators (outcome metrics) creates a complete performance picture. This dual perspective enables both proactive adjustments and retrospective evaluation.
Analyzing Data and Drawing Conclusions
Data analysis reveals the story behind the numbers. Sophisticated pattern recognition uncovers unexpected relationships between channel interactions and business outcomes. These insights frequently challenge assumptions, revealing hidden opportunities for optimization.
Longitudinal analysis proves particularly valuable, showing how customer behaviors evolve as omnichannel maturity increases. This perspective helps justify continued investment by demonstrating compounding returns over time.
Reporting and Communicating Results
Effective reporting translates complex data into compelling narratives. Visual storytelling through dashboards and infographics makes performance trends immediately graspable for diverse stakeholders. The most impactful reports highlight not just what happened, but what actions the data suggests.
Transparent communication of both successes and learning opportunities fosters organizational trust in data-driven decision making. This culture of openness accelerates continuous improvement cycles.
Analyzing Data and Optimizing for Maximum Impact
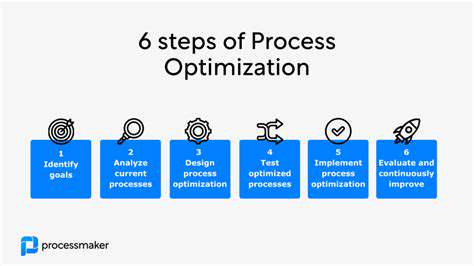
Data Collection Strategies
Smart data gathering requires balancing comprehensiveness with relevance. The most valuable datasets combine structured transactional data with unstructured behavioral signals across channels. This multidimensional approach captures both what customers do and why they might be doing it.
Progressive organizations implement always-on data collection frameworks that adapt as customer behaviors evolve. These systems prioritize data quality at the point of capture, reducing cleaning burdens downstream.
Data Cleaning and Preprocessing
Data refinement is where analytics transitions from art to science. Advanced techniques like anomaly detection algorithms automatically surface inconsistencies for review. This rigorous quality control ensures subsequent analysis rests on reliable foundations.
Context-aware imputation methods now allow missing data points to be estimated with remarkable accuracy, preserving dataset integrity without distorting underlying patterns.
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
EDA represents the detective work of data science. Modern visualization tools enable analysts to interview data through interactive exploration. These dynamic investigations frequently uncover insights that pre-defined reports would miss.
Advanced correlation analysis reveals not just direct relationships, but how variables interact in complex systems. This understanding proves invaluable when optimizing interconnected omnichannel ecosystems.
Statistical Modeling and Inference
Contemporary modeling techniques account for the fluid nature of omnichannel interactions. Ensemble methods combine multiple models to improve prediction accuracy across diverse customer segments. These approaches handle the inherent variability in cross-channel behavior patterns.
Interpretability remains paramount—the best models provide clear explanations for their outputs, enabling business users to act on insights with confidence.
Optimization Strategies
Continuous improvement requires intelligent iteration. Modern optimization leverages machine learning to test thousands of potential adjustments, identifying high-impact improvements. This automated experimentation accelerates the path to optimal performance.
The most effective optimizations consider both immediate metrics and long-term customer relationship impacts, ensuring short-term gains don't undermine lifetime value.