Countries around the world have been actively updating their data privacy laws to address growing concerns about personal information security. The global patchwork of data protection rules creates both opportunities and challenges for businesses operating internationally. Companies that fail to adapt to these varying requirements risk facing substantial fines and losing customer trust.
Legal frameworks differ significantly across regions, with some favoring strict individual rights while others emphasize business flexibility. This diversity forces multinational corporations to develop nuanced compliance strategies. Successful navigation of this complex terrain demands specialized legal expertise and ongoing monitoring of regulatory changes.
The Impact of AI and Machine Learning on Data Privacy
Artificial intelligence systems require massive amounts of training data, much of which may include personal details. This creates tension between technological advancement and privacy protection. Organizations must balance innovation with ethical considerations when implementing AI solutions.
Automated decision-making systems in areas like credit scoring have raised valid concerns about systemic bias. Developing comprehensive oversight mechanisms represents the best approach to maintaining fairness in algorithmic processes. Transparency about data usage and decision criteria helps build public confidence.
The Role of Data Security in Protecting Personal Information
Effective information security requires multiple layers of protection, from encryption to access management. Regular vulnerability assessments help identify potential weaknesses before they can be exploited.
The financial and reputational costs of data leaks can be catastrophic. Preparation through rigorous security protocols and detailed response plans significantly reduces breach impacts. Early detection systems combined with swift containment measures can prevent minor incidents from becoming major crises.
Emerging Trends in Data Protection
Smart devices and interconnected systems generate unprecedented amounts of personal data daily. This expansion of the Internet of Things creates both opportunities and security challenges.
Cloud-based solutions demand special attention to data residency and jurisdiction issues. Forward-thinking organizations are developing flexible privacy frameworks that can adapt to technological and regulatory changes. Building trust through transparent data practices has become a key competitive advantage.
Navigating the California Consumer Privacy Act (CPRA)
Understanding the Core Principles of CPRA
The California Privacy Rights Act represents a major shift in consumer data rights for businesses serving California residents. It establishes specific obligations regarding data collection transparency and user control. Retailers must completely rethink their data handling processes to avoid potentially devastating penalties.
CPRA empowers consumers with unprecedented access to and control over their personal information. Businesses must provide clear explanations of data practices and simple opt-out mechanisms. The law requires companies to maintain detailed records of data processing activities and consumer requests.
Implementing CPRA Compliance in E-commerce
Online retailers face particular challenges in meeting CPRA requirements across complex digital ecosystems. Compliance must be embedded in every stage of the customer journey, from account creation to checkout.
User interfaces should make privacy choices intuitive rather than buried in fine print. Investment in automated request management systems pays dividends in compliance efficiency and customer satisfaction. Regular staff training ensures consistent implementation across departments.
The regulatory landscape continues evolving rapidly. Establishing cross-functional privacy teams helps organizations stay ahead of both current requirements and future developments. Proactive compliance becomes a brand differentiator in privacy-conscious markets.
Developing a Comprehensive Data Compliance Strategy
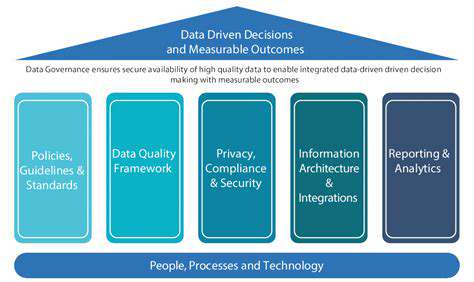
Data Collection Strategies
Effective data governance begins with clear identification of information needs. Precise definition of data requirements prevents collection of irrelevant information and focuses resources on high-value assets. Documenting collection methodologies ensures consistency and auditability.
Combining quantitative and qualitative approaches often provides the most complete understanding. Method selection should consider both immediate analysis needs and potential future uses of the data. Ethical collection practices build long-term stakeholder trust.
Data Storage and Management
Modern data architectures must balance accessibility with robust security controls. Classification systems enable appropriate protection levels based on sensitivity. Implementing comprehensive backup and recovery procedures safeguards against catastrophic data loss.
Regular data hygiene practices maintain information quality over time. Systematic validation checks catch errors before they propagate through analytics processes. Version control mechanisms preserve data integrity during collaborative work.
Data Analysis Techniques
Analytical approaches should align with both data characteristics and business objectives. Proper technique selection separates meaningful signals from statistical noise. Documentation of analytical assumptions supports reproducibility and peer review.
Visual presentations should emphasize clarity over complexity. Well-designed dashboards transform raw metrics into actionable business intelligence. Interactive elements allow users to explore data relationships dynamically.
Data Interpretation and Reporting
Contextual understanding prevents misinterpretation of analytical results. Critical evaluation of findings against real-world conditions validates their practical significance. Clear documentation of limitations builds credibility with stakeholders.
Tailored reporting formats maximize impact for different audiences. Executive summaries should highlight key insights while supporting documentation provides methodological rigor. Actionable recommendations bridge the gap between analysis and implementation.